The Unspoken Risks of NOT Retiring Early
9 min read[Editor’s Note: If you’re a resident who’s looking to jumpstart your financial education before you begin attendinghood, drop everything right now and make plans to attend our free Resident Webinar with WCI Founder Dr. Jim Dahle and StudentLoanAdvice.com co-founder Andrew Paulson on May 29 at 6pm MT. You’ll learn how to manage and optimize your student loans, get started with saving and investing, and learn how to be financially successful. This webinar literally could be worth millions of dollars to you! Make sure to register today and begin learning how to navigate your successful financial journey in the next phase of your career.]
 By Dr. Jim Dahle, WCI Founder
By Dr. Jim Dahle, WCI Founder
Investing is more about risk control than it is about chasing returns. When it comes to early retirement, most people are aware of the main risk—running out of money before you run out of time. This keeps some people in the workforce worrying longer than they probably should, and it is known as “one more year syndrome.” It’s true that the numbers all look better a year or five years or, especially, 10 years later. You have more time to contribute to your retirement accounts, more time for compound interest to work its magic, a larger Social Security benefit (either from more contributions or from delaying the receipt of benefits or both), and less time left in life for that nest egg to support you.
There are non-financial risks, too. You might get divorced. Perhaps you and your spouse don’t get along all that well, and when you retire and are now at home for an extra 40-60 hours a week, the relationship implodes. Maybe you get bored (although I suppose you could go back to work if that’s really an issue). I’ve seen that happen every now and then. Maybe you lose the social contact that you were getting from work and become lonely and bitter. Or maybe you feel like you’re not contributing anything useful to the world. These are all very real risks of early retirement, but we’re not going to discuss those today.
However, there are also some risks, even unspoken risks, of NOT retiring early. Today, we’ll discuss six of these risks.
#1 Early Mortality
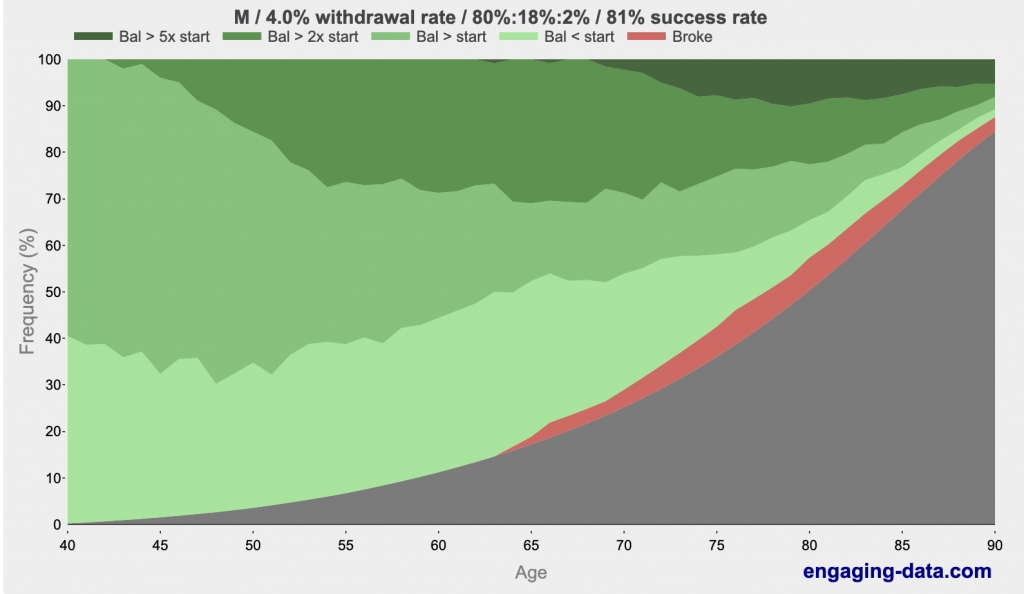
People routinely plan to be retired for 30 years, like in the classic Trinity Safe Withdrawal Rate study. Early retirees figure they might need another decade or two added on to that. A 40-year-old retiree might need their portfolio to last 55 years. Or more. However, there is also the possibility that they die next year. Consider the classic graph/calculator titled “Rich, Broke, or Dead?”
The thing everybody fears, going broke, is just a tiny sliver of what could happen to people. The actual occurrence of this event is even more rare than this graph shows since most people will make adjustments long before they actually go broke. What should people fear? That big black thing. That’s right: dying. Sure, the risk is pretty low in your early 50s, but it isn’t zero. It certainly isn’t zero in your 70s and 80s. The average life expectancy of a 50-year-old male is 30 years. That means half of them die in less than 30 years. If you’re one of those who will die in 10-15 years but you saved and then spent in retirement as though you needed that nest egg to last 30, you definitely “oversaved.” You probably could have successfully retired five years earlier without any issues. If you knew you only had 15 more years on the planet, how many of them do you want to spend working full time and how many of them do you want to spend retired? Early mortality can be a risk of NOT retiring early.
More information here:
Functional Longevity: What Use Is Retirement If You Can’t Move and Think?
The Happiness Index: Mine Required My Own Version of Retirement
#2 Extended Morbidity
You know what else can happen? You can get sick, injured, or even disabled. I had a family member who was an active outdoorsman. He worked as an employee until 58 or so. Then, he stuck around working hard as an independent contractor “double-dipping” on his pension while getting paid more than ever before and saving up a substantial nest egg between 58-65 before fully retiring over the course of a couple of years. By the time he was fully retired, he could no longer do the things he loved to do, which he had been planning to do more of in retirement.
There are “seasons” in your life when you can do some things. If you don’t do the things that apply to that season while you are in it, you can’t go back and do them later. Consider reading books to your kids before they go to bed. That’s a lot of fun at 6 years old. They’re not interested at 16. You missed it. Likewise, you may want to do some things in your life that need to be done in your 40s, 50s, 60s, or 70s. If you miss them, it’s too late. To make matters worse, the ability to do those things often leaves you unexpectedly. You hurt your hip at 52 and now you can’t rock climb, ski, or play softball, even though you were planning to do those things into your 60s.
People come down with more and more medical problems with each decade of life. In my 30s, it was GERD. In my 40s, it was short arm syndrome (eventually my arms became so short I had to start wearing reading glasses) and chronic low back pain. What’s going to happen in my 50s? Osteoarthritis? Heart disease? Diabetes? What about my 60s? Knee replacements? A-fib? A stroke? You just don’t know. We all want “compressed morbidity.” That is, we want to be perfectly healthy until a month before we die at 98. Guess what? Most people don’t get that. Our medical innovations over the last few decades are far better at keeping us alive longer than they are at compressing morbidity. Extended morbidity can be a risk of not retiring early.
#3 Dementia
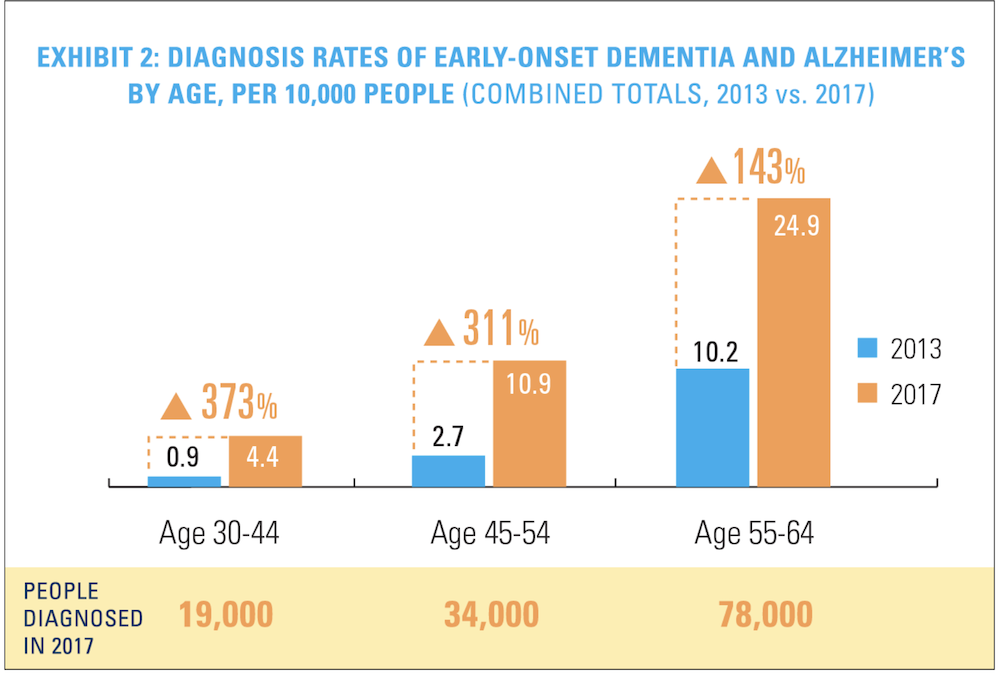
While this one could have been included under #2, it can be so severe that it robs you of your long-planned retirement even if you have excellent physical health. It’s a horrible trick really, robbing someone of their memories at the end of their long life when it is so much harder to make new ones. Maybe you’ve got 30 years of life left but only 18 without dementia. How many of them do you want to spend working? It’s not like dementia only affects those in their 70s, 80s, and 90s either. Early onset dementia is becoming MORE common, not less common.
People used to fear uncurable infectious diseases like plague and polio. Now, people rarely get those and survive them when they do. But dementia remains stubbornly difficult to slow, much less cure. Dementia can be a risk of not retiring early.
#4 Time with Loved Ones
I had a partner who retired in his early 50s. He was pretty frugal, and he had a bit of a windfall from selling a small medical devices company so he could afford to retire. When asked why he was retiring early, he cited lots of reasons (including liability), but I think the main one was that his two kids were in high school and he didn’t want to miss ANY time with them. Whether it’s time with an aging parent, time with kids who will soon leave home, or just time with your spouse (unless you’re lucky enough to work with them), time at work is time you’re not spending with them. Losing time with loved ones is an unspoken risk of not retiring early.
More information here:
Are Physicians Who Retire Early Abusing the System That Made Them Rich?
Dealing with the Guilt of Early Retirement
#5 You May Lose Your Ability (or Desire) to Work

While doctors can generally find new work (at least within six months) if they somehow get fired, there are exceptions—especially if you lost your job for a reason that prevents you from getting another one but doesn’t qualify for disability insurance benefits. Try getting a new job after multiple medical board complaints, a sexual harassment lawsuit, or committing a crime like doctoring medical records or assaulting someone. Malpractice insurance doesn’t pay. Disability insurance doesn’t pay. If you’re not financially independent when it happens, you’re up a creek without a paddle. If you’re not aiming at early retirement, you spend more of your life exposed to financial risks that may or may not show up. You thought you had 10 more years to save for retirement, and now you don’t.
You might also just become severely burned out. Or maybe you do become disabled, but you never could get disability insurance. While these are all risks of not being financially independent, that often goes along with early retirement and not just in the acronym FIRE.
Leif Dahleen, an early retired anesthesiologist, described it thusly:
“For the love affair [with your job] to last, two conditions must remain true.
First, the job cannot change in a way that causes you to love it less. Any change in your work schedule, obligations, compensation, benefits, or work colleagues that negatively impacts you can leave you feeling less amorous.
Second, you and the things you value and prioritize must remain indefinitely steady. The odds of this being true over a career lasting even a decade or two are on par with the chances that I fail to survive long enough to see this article published.
Think about who you were five, 10, or 20 years ago. What mattered most to you then? Who were the most important people in your life? How did you balance a career with family, hobbies, and other outside interests? How has that changed? Being excited about or even content with the job you’ve got is a lot better than despising the work you do. Just realize that as time goes on, the odds of remaining in love with your job will likely diminish. With a shred of luck and some proper planning, your relationship with your career will not be of the ‘’til death do us part’ variety. It’s not supposed to be.”
Losing your ability or desire to work is a major risk of not retiring early.
#6 Lost Financial Benefits
Early retirees take advantage of an extended period of time between when they stop working and when they start collecting their Social Security, often at age 70. If you retire at 65, you only have five years before 70. If you retire at 50, you’ve got 20 years. What can you do in those 20 years? You can do very low-cost Roth conversions. You can take advantage of the 0% qualified dividends/LTCGs brackets. You can qualify for a PPACA subsidy. You’ll spend more of your life in the lower tax brackets. You can pursue an encore career or side gig. Few traditional retirees are going to have the same benefits. Missing out on those is a risk of not retiring early.
If you’re a high earner who has spent much time on this site, you already know, or soon will, that time is far more precious than money. You can get to the point where you have more money than you will need for the rest of your life, and time will become the limiting resource. Very few people on their deathbed regret not spending enough time at work. Retirement is often composed of “go-go years” (perhaps 65-75), “slow-go years” (perhaps 75-85), and “no-go years” (85-95). Early retirement allows you to double or even triple your “go-go years.” Missing out on that is a pretty big unspoken risk of not retiring early.
Did you know our White Coat Investors Facebook Group has more than 96,000 members? Get social with us and join the conversation today!
What do you think? Are you planning on an early retirement? Why or why not? What do you see as the risks of retiring early and, conversely, NOT retiring early? Comment below!